Produces diagnostic plots on the result of an mlmc.test function call.
Usage
# S3 method for class 'mlmc.test'
plot(x, which = "all", cols = NA, ...)Arguments
- x
an
mlmc.testobject as produced by a call to themlmc.testfunction.- which
a vector of strings specifying which plots to produce, or
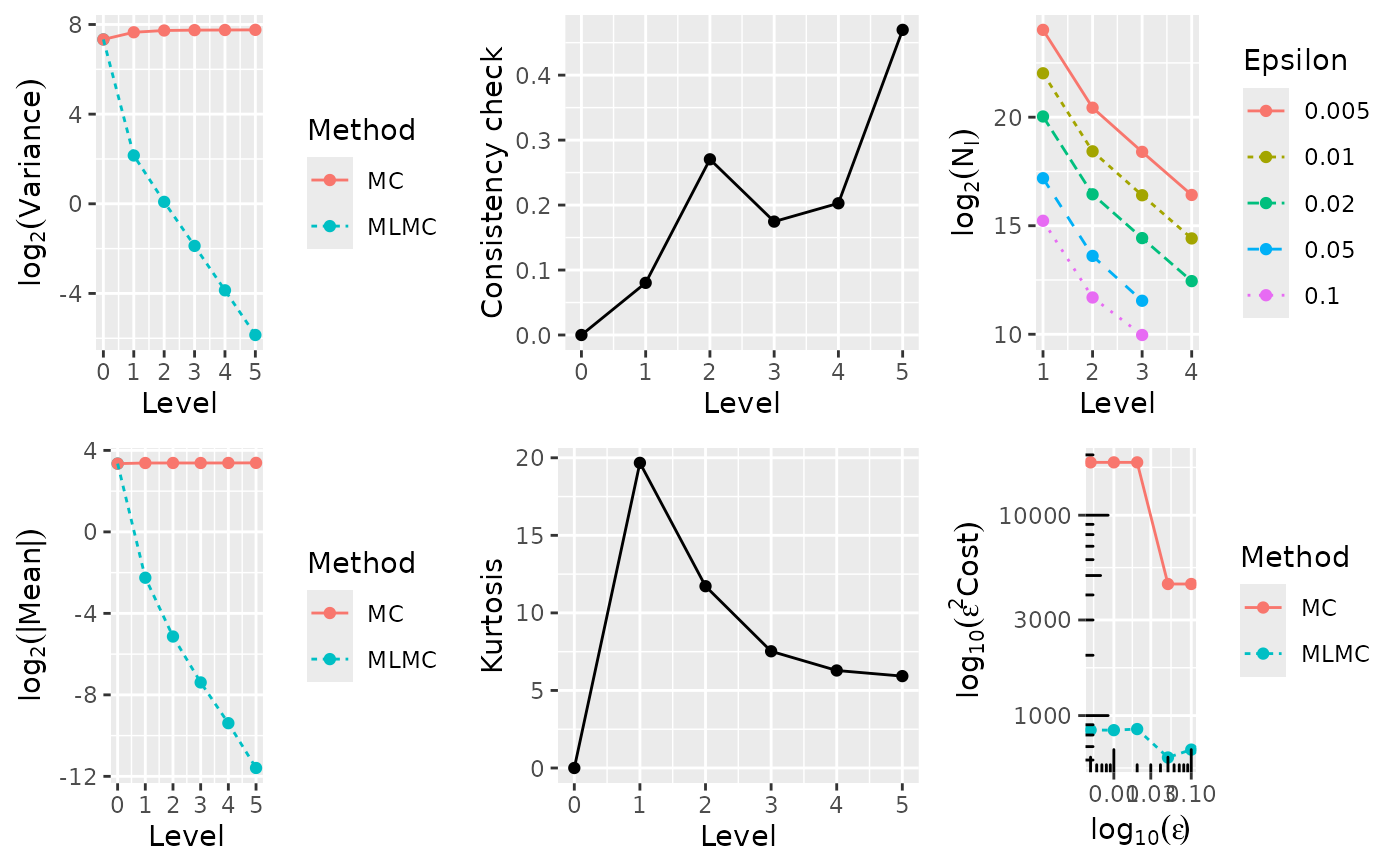
"all"to do all diagnostic plots The options are:"var"= \(\log_2\) of variance against level;"mean"= \(\log_2\) of the absolute value of the mean against level;"consis"= consistency against level;"kurt"= kurtosis against level;"Nl"= \(\log_2\) of number of samples against level;"cost"= \(\log_{10}\) of cost against \(\log_{10}\) of epsilon (accuracy).
- cols
the number of columns across to plot to override the default value.
- ...
additional arguments which are passed on to plotting functions.
Details
Most of the plots produced are relatively self-explanatory. However, the consistency and kurtosis plots in particular may require some background. It is highly recommended to refer to Section 3.3 of Giles (2015), where the rationale for these diagnostic plots is addressed in full detail.
References
Giles, M.B. (2015) 'Multilevel Monte Carlo methods', Acta Numerica, 24, pp. 259–328. Available at: doi:10.1017/S096249291500001X .
Examples
# \donttest{
tst <- mlmc.test(opre_l, N = 2000000,
L = 5, N0 = 1000,
eps.v = c(0.005, 0.01, 0.02, 0.05, 0.1),
Lmin = 2, Lmax = 6,
option = 1)
#>
#> **********************************************************
#> *** Convergence tests, kurtosis, telescoping sum check ***
#> *** using N = 2e+06 samples ***
#> **********************************************************
#>
#> l ave(Pf-Pc) ave(Pf) var(Pf-Pc) var(Pf) kurtosis check cost
#> ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#> 0 1.0204e+01 1.0204e+01 1.6111e+02 1.6111e+02 0.0000e+00 0.0000e+00 1.0000e+00
#> 1 2.0978e-01 1.0419e+01 4.4282e+00 2.0086e+02 1.9992e+01 7.7067e-02 4.0000e+00
#> 2 2.7917e-02 1.0437e+01 1.0597e+00 2.1218e+02 1.1899e+01 1.5001e-01 1.6000e+01
#> 3 5.9321e-03 1.0458e+01 2.7342e-01 2.1576e+02 7.6521e+00 2.2633e-01 6.4000e+01
#> 4 1.6115e-03 1.0447e+01 6.8853e-02 2.1627e+02 6.2409e+00 1.9702e-01 2.5600e+02
#> 5 3.9072e-04 1.0470e+01 1.7246e-02 2.1694e+02 5.9172e+00 3.5425e-01 1.0240e+03
#>
#> ******************************************************
#> *** Linear regression estimates of MLMC parameters ***
#> ******************************************************
#>
#> alpha = 2.225166 (exponent for MLMC weak convergence)
#> beta = 1.995258 (exponent for MLMC variance)
#> gamma = 2.000000 (exponent for MLMC cost)
#>
#> *****************************
#> *** MLMC complexity tests ***
#> *****************************
#>
#> eps value mlmc_cost std_cost savings N_l
#> -----------------------------------------------------------
#> 0.0050 1.0444e+01 4.595e+07 2.953e+09 64.26 19869061 1645394 402146 101574 25655
#> 0.0100 1.0439e+01 8.500e+06 1.841e+08 21.66 4272282 353369 87864 22003
#> 0.0200 1.0449e+01 2.095e+06 4.603e+07 21.98 1060005 88011 21310 5336
#> 0.0500 1.0447e+01 2.384e+05 1.811e+06 7.60 141888 12734 2846
#> 0.1000 1.0365e+01 6.600e+04 4.526e+05 6.86 38068 2984 1000
#>
tst
#>
#> **********************************************************
#> *** Convergence tests, kurtosis, telescoping sum check ***
#> *** using N = 2e+06 samples ***
#> **********************************************************
#>
#> l ave(Pf-Pc) ave(Pf) var(Pf-Pc) var(Pf) kurtosis check cost
#> ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#> 0 1.0204e+01 1.0204e+01 1.6111e+02 1.6111e+02 0.0000e+00 0.0000e+00 1.0000e+00
#> 1 2.0978e-01 1.0419e+01 4.4282e+00 2.0086e+02 1.9992e+01 7.7067e-02 4.0000e+00
#> 2 2.7917e-02 1.0437e+01 1.0597e+00 2.1218e+02 1.1899e+01 1.5001e-01 1.6000e+01
#> 3 5.9321e-03 1.0458e+01 2.7342e-01 2.1576e+02 7.6521e+00 2.2633e-01 6.4000e+01
#> 4 1.6115e-03 1.0447e+01 6.8853e-02 2.1627e+02 6.2409e+00 1.9702e-01 2.5600e+02
#> 5 3.9072e-04 1.0470e+01 1.7246e-02 2.1694e+02 5.9172e+00 3.5425e-01 1.0240e+03
#>
#> ******************************************************
#> *** Linear regression estimates of MLMC parameters ***
#> ******************************************************
#>
#> alpha = 2.225166 (exponent for MLMC weak convergence)
#> beta = 1.995258 (exponent for MLMC variance)
#> gamma = 2.000000 (exponent for MLMC cost)
#>
#> *****************************
#> *** MLMC complexity tests ***
#> *****************************
#>
#> eps value mlmc_cost std_cost savings N_l
#> -----------------------------------------------------------
#> 0.0050 1.0444e+01 4.595e+07 2.953e+09 64.26 19869061 1645394 402146 101574 25655
#> 0.0100 1.0439e+01 8.500e+06 1.841e+08 21.66 4272282 353369 87864 22003
#> 0.0200 1.0449e+01 2.095e+06 4.603e+07 21.98 1060005 88011 21310 5336
#> 0.0500 1.0447e+01 2.384e+05 1.811e+06 7.60 141888 12734 2846
#> 0.1000 1.0365e+01 6.600e+04 4.526e+05 6.86 38068 2984 1000
#>
plot(tst)
 # }
# }
